Instead of managing a vast amount of user names and passwords we want one digital identity, a “passport” reusing login information and giving us secure and easy access to all the services and resources we require to study, do research, and collaborate with colleagues across borders.
A lake of lava lies directly below a small South Korean island. The simulations that led to this discovery were performed on supercomputer Piz Daint at the Swiss National Supercomputing Center and the now decommissioned Huygens, the national supercomputing center of SURF in the Netherlands.
The Nordic research and education networks are preparing to put a whole new network infrastructure in place for EISCAT 3D, as the powerful new radar is situated in remote northern Scandinavia to assure a minimum of background noise. For the next 35 to 40 years to come, it will be the centerpiece of the international network of instruments monitoring the Earth’s upper atmosphere and space environment.
MinE is an international project to search for the genetic causes of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis), a deadly neurodegenerative disease. Thanks to an enormous computing facility and the best network connection, the MinE project can generate better results.
Technology is rapidly changing the way athletes and sports coaches work together. Accurate feedback and reliable assessment techniques are the main ingredients to maintain and improve performances or to effectively recover from sport injuries. Remote sensing and data sonification, underpinned by high-capacity connectivity, can improve standard data analysis techniques.
Because of its sheer size, a pipe organ is bound to the location where it’s situated, making it very rare for organists to be able to play together. Until now. A magic moment occurred at theTNC16 research and education network conference in Prague: two organs more than 2000 km apart will play a concert together, thus creating a completely new musical experience.
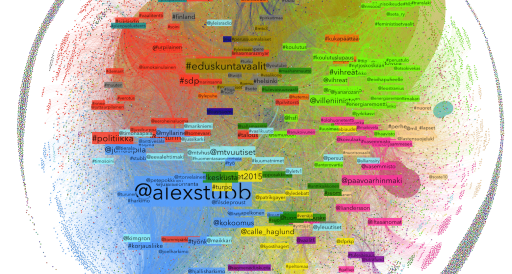
As social media like Facebook and Twitter become increasingly influential in the decision making of the voters, social scientists take an interest in scrutinizing, how discussions and debates emerge and evolve in the intersection between traditional media and social media. Finnish researchers have enlisted a supercomputer to crack the data.
Swedish information scientists collaborate with global pharmaceutical company and data mining experts to forecast technologies related to intelligent pharmaceuticals.
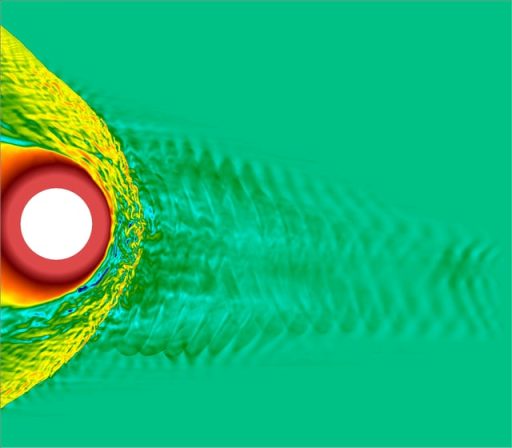
As computer simulations go, Vlasiator is as huge as they come. Developing Vlasiator, Minna Palmroth, professor at the Finnish Meteorological Institute, has succeeded in doing what many of her colleagues thought impossible: Simulating weather in near-Earth space, showing how solar wind affects us, using high performance computing and high speed networks to do so.