The Research and Education Network for Uganda is helping one of the country’s universities, the Ugandan Christian University offer PhD and Master of Journalism and Media Studies Progammes online in collaboration with the University of Kwazulu Natal in South Africa and the NLA University College in Norway.
Biotelemetry technology for wildlife and fish monitoring has evolved tremendously since the 1990’s: from moose and reindeer wearing collars with primitive radio transmitters weighing several kilos, to salmon with miniscule bio-sensors, and eagles wearing solar powered GPS-backpacks. But there’s a gap between the volumes of data available and the tools for handing it.
The Indian summer monsoon is a manifestation of complex interactions between land, ocean and atmosphere and the simulation of its mean pattern and its variability on inter-annual scales is one of the challenging problems in climate studies. The correct prediction of this complex phenomenon is vital to national planning and economic policy making.
“Diseases don’t know boundaries or country codes, we have to build systems that allow researchers to collaborate internationally,” says Professor Richard Sinnott. With that goal in mind, he established the endocrine genomics virtual laboratory – endoVL, which allows researchers to draw on large enough cohorts to conduct studies with real statistical power.
As research becomes increasingly data-intensive, researchers have to sharpen their data management skills. The Data Intensive Research Initiative of South Africa (DIRISA) lends a helping hand, by providing an online Data Management Planning tool, for sound collection, management, accessibility and preservation of research data.
The Indian Institutes of Technology, IITs, are the flagships of Indian engineering education. Getting into an IIT is the dream of every aspiring engineer in India, and each year over a million people take the entrance exam. But competition is fierce: with only 10.000 (2%) passing the exam, the IITs are among the institutes with the lowest acceptance rate worldwide.
Doñana National Park in Andalusia Spain is one of the world’s most fascinating nature reserves, a mosaic of ecosystems and home to unique and endangered species. The Park is connected to LifeWatch, a joint European e-infrastructure for biodiversity and ecosystem research, which enables scientists to access a vast array of data from multiple resources in real time to learn about the environment.
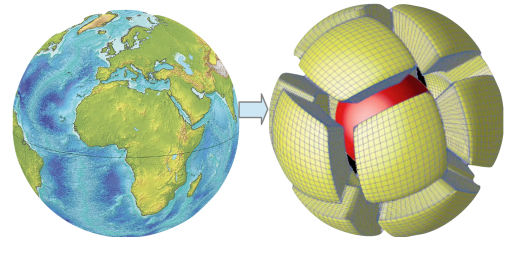
The Earth is a complex and dynamic system, and the inner workings of our planet have serious catastrophic potential for humans in the form of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Using e-infrastructure resources and supercomputers, a research group at the University of Oslo, Norway, is investigating the link between processes which occur deep in Earth’s interior, and those at the surface.
Participants at the 3rd TEIN/APAN Dengue Fever workshop on 24 January in Manila reaffirmed their commitment to join forces with research and education networks to combat Dengue Fever and other infectious diseases such as Zika. Plans include developing a digital platform to exchange data and working towards an outbreak prediction model.
A full set of one person’s DNA data requires a stack of 50 DVDs while a large study with 1,000 patients can be hundreds of terabytes of data. This makes it impractical to transfer genomic data using traditional methods, challenging to store it, and virtually impossible to use it without advanced research and education networks like CANARIE, sophisticated software tools, and high performance computing facilities.
Think of a dance performance in which the dancers, instead of sharing the same stage, are in different cities or even other continents. That is the mission of telematics dance, approaching dancers who are not necessarily in the same physical space, and creating other experience relations with the body and technological resources.
Wouldn’t it be nice to be able to solve problems before they occur? Unfortunately, predicting the future is difficult when it comes to complex systems like industrial production lines or wind farms. But a group of European researchers and industry experts have joined forces to build a system of sensors and computers that could help us solve problems in high tech environments.